In today’s article Health Bunker will cover Amino Acids. This will be a short overview of these nutrients, giving examples of the importance of essential and nonessential amino acids in the human body. We will then do follow up articles covering more detail.
How many Amino Acids Are there?
Amino Acids are referred to as the building blocks of proteins. They are chemical compounds that have many different roles to play in the human body. Amino acids are needed for vital functions like the building of proteins and synthesis (production) of hormones and neurotransmitters.
Amino acids can be taken as supplements to enhance athletic performance and recovery or for mood. Amino acids are organic compounds made up from, nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and a side chain group.
Our bodies require 20 amino acids to grow and function correctly. Although all 20 amino acids are important for our health and wellbeing not all are classified as essential. There are 3 amino groups:
- Essential Amino Acids
- Nonessential Amino Acids
- Conditional Amino Acids
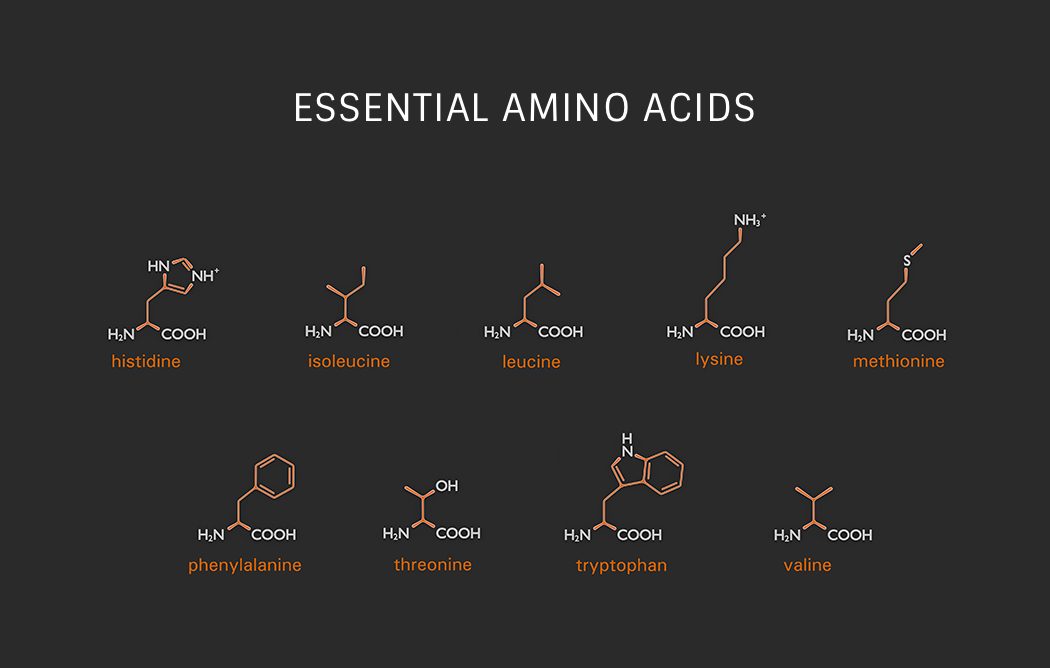
Essential Amino Acids
There are 9 essential amino acids. Essential amino acids must be obtained from our diet, unlike nonessential amino acids that are produced by our body.
- Histidine
- Isoleucine
- Leucine
- Lysine
- Methionine
- Phenylalanine
- Threonine
- Tryptophan
- Valine
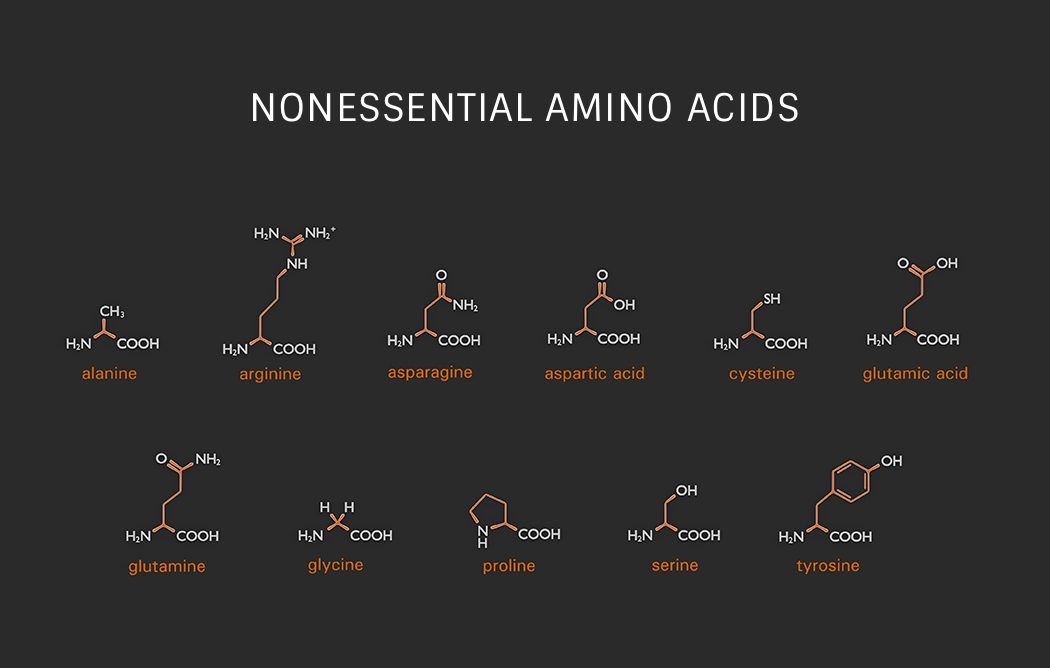
Nonessential Amino Acids including;
Our bodies produce these amino acids even if we don’t acquire them from food. Nonessential amino acids include;
- Alanine
- Arginine
- Asparagine
- Aspartic acid
- Cysteine
- Glutamic acid
- Glutamine
- Glycine
- Proline
- Serine
- Tyrosine
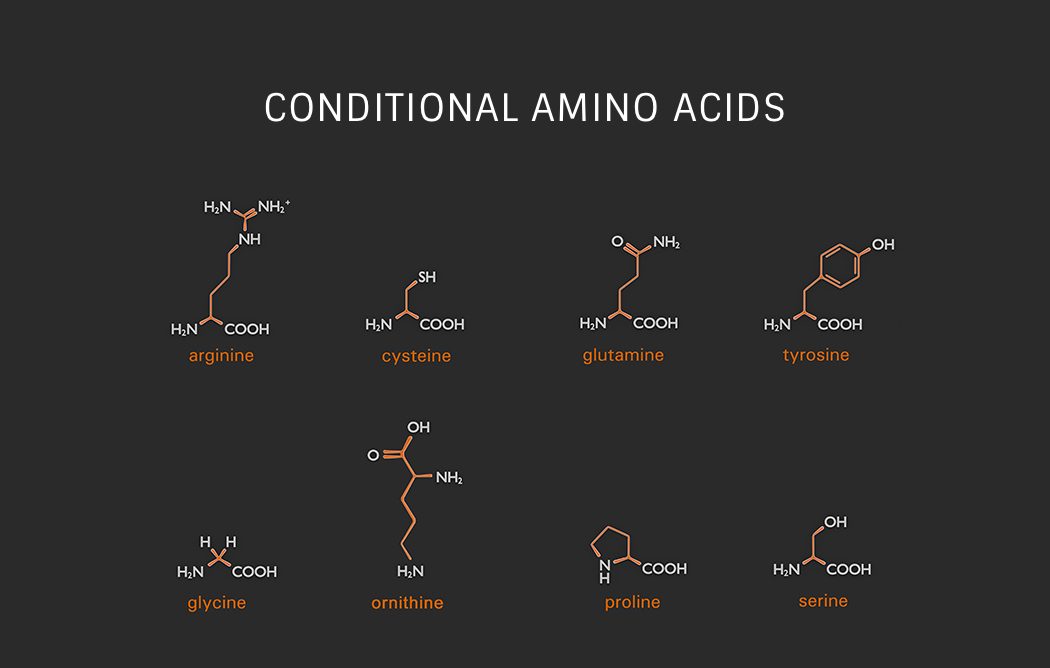
Conditional Amino Acids
These amino acids are usually nonessential, except in times of stress or illness. And they include;
- Arginine
- Cysteine
- Glutamine
- Tyrosine
- Glycine
- Ornithine
- Proline
- Serine
What do Essential Amino Acids Do?
Histidine produces histamine, which is a neurotransmitter that is vital for immune response, digestion, sexula functions, and sleep cycles. Histidine is essential for maintaining the myelin sheath which is a protective barrier surrounding our nerve cells.
Isoleucine is a branched chain amino one of 3. Isoleucine is involved in muscle metabolism and is heavily concentrated in muscle tissues. It is essential for immune function, hemoglobin production and energy regulation.
Leucine is another of the 3 branched chain amino acids. Critical for protein synthesis and repair of muscles. Leucine also regulates blood sugar levels, stimulates healing and produces growth hormones.
Lysine is another essential amino acid involved in proteins, enzymes and hormone production. It plays a key role in calcium absorbtion, energy production, immune function, and the production of collagen and elastin.
Methionine is important for metabolism and detoxification. Methionine is essential for tissue growth and zinc and selenium, and mineral absorption that are vital for good health.
Phenylalanine is one of the precursors for neurotransmitters tyrosine, dopamine, epinephrine and norepinephrine. Phenylalanine plays an important role in the structure of proteins and enzymes, and also the production of other amino acids.
Threonine is a part of structural proteins like collagen and elastin. These keep skin and connective tissue healthy. Threonine plays a role in immune functions and metabolism.
Tryptophan helps with our nitrogen balance, and is a precursor to serotonin, a neurotransmitter which regulates appetite, mood and sleep.
Valine is the last of the 3 branched chain amino acids, meaning it has a chain branching off it’s molecular structure. Valine stimulates muscle growth and regeneration is involved with energy production.
Health Bunker
Amino Acids are required in many essential chemical reactions in the body. If you look at what the roles of these amino acids are you can begin to see the problems that are caused when we are deficient. Amino acids are the precursor to hormone functions and are required for immune function too.
For more information contact us via the website.
Eat Well. Be Well.
Dom & Nic
It’s your life. Own it.
*Disclaimer – Please note, we are not Doctors or trained medical professionals. We are not giving medical advice. Check with your Doctor or health practitioner before trying anything.
References and Sources of Information;
Wikipedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carboxylic_acid/carboxyl_group
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Side_chain
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amino_acid
Health Line negatively charged
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/essential-amino-acids
Medlineplus
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002222.htm
Medicine Net Carbon Atom
https://www.medicinenet.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=22839
Receive Updates
Receive the latest articles as they’re published.